Trade Members Get 10% Off. Sign Up Today

Understanding LED Dimming: A Guide To Modern Light Control | UltraLEDs
Controlling brightness is an essential skill in every lighting designer’s toolbox. LEDs dim differently from traditional tungsten or halogen lamps.
As LED lighting becomes increasingly common, it’s important to understand how to manage dimming using modern lighting components to achieve optimal results.
In this guide, we’ll explore the principles behind LED dimming, address practical solutions to challenges like flickering and voltage drop, and delve into advanced protocols such as DMX.
Insights from George Davies, Director of Pecelec Studio Ltd, are included to provide expert guidance for professional installations.

How Are LEDs Dimmed?
LED dimming works by controlling the power delivered to the lights, either by adjusting voltage or current.
LEDs require specialised dimming methods, such as PWM and CCR, to maintain consistent colour and performance while adjusting brightness.
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
PWM dims LEDs by rapidly switching them on and off at high frequencies, creating the illusion of continuous dimming. The ratio of "on" to "off" time (duty cycle) determines brightness:
- Longer “on” times produce brighter light.
- Shorter “on” times create dimming effects.
PWM is widely used because it’s simple, compatible with both CV and CC systems, and delivers predictable results. However, it can cause flickering at lower brightness levels or interference in environments with strict EMI controls.
Triac Dimming (Phase-Cut)
Triac dimming reduces brightness by cutting part of the AC waveform. Commonly used in residential settings, it works with compatible LEDs but may cause flickering or noise if components are mismatched.
Constant Current Reduction (CCR)
CCR dims LEDs by reducing the current flowing through the circuit. This method ensures flicker-free, stable dimming but is only compatible with CC systems.
While it’s excellent for environments requiring minimal EMI, CCR can result in less accurate dimming for certain colours, particularly whites.

Types of LED Systems
Understanding whether your system uses constant voltage (CV) or constant current (CC) is crucial, as this determines the appropriate dimming method:
- Constant Voltage (CV): Operates at a fixed voltage (e.g., 12V or 24V). PWM is the only method suitable for dimming these systems, offering flexibility for applications like LED strip lighting.
- Constant Current (CC): Maintains a constant current (e.g., 350mA or 700mA) while varying voltage. Both PWM and CCR can be used to dim CC systems, allowing for precise control in high-performance installations.
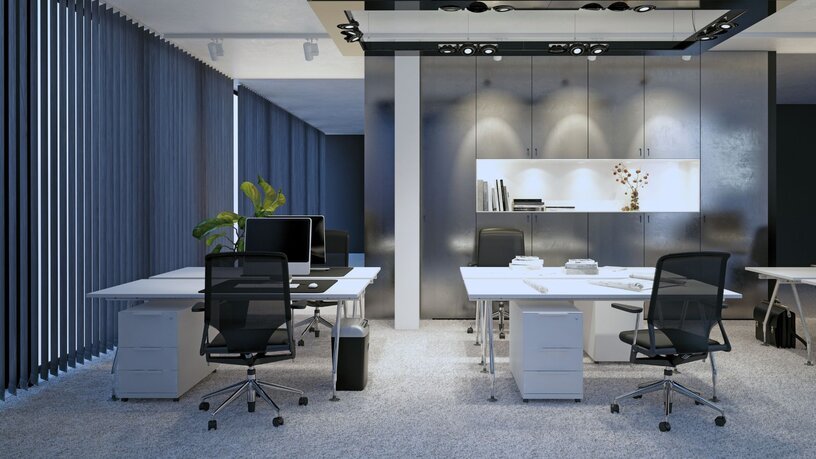

PWM vs CCR
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM):
- Compatible with both constant voltage (CV) and constant current (CC) systems, offering greater versatility across various projects.
- Can cause flickering at lower brightness levels, particularly when recorded on camera.
- May introduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) in sensitive environments or produce occasional audible noise.
- Ideal for dynamic projects like RGB or pixel-based lighting, where flexibility is required.
Constant Current Reduction (CCR):
- Exclusive to constant current (CC) systems, providing stable, flicker-free dimming for applications where consistency is critical.
- Avoids electrical interference, making it suitable for environments with strict EMI controls.
- May struggle with dimming for certain colours, such as whites, compared to PWM.
- Best for specialised environments requiring steady and reliable dimming rather than flexibility.

Types Of LED Dimming Modules
Dimming modules vary in complexity and suitability for different applications. Below are the main types to consider:
Inline Dimming
- A straightforward and effective solution for maintaining a fixed brightness that rarely changes.
- Ideal for simple setups where no ongoing adjustments are needed.
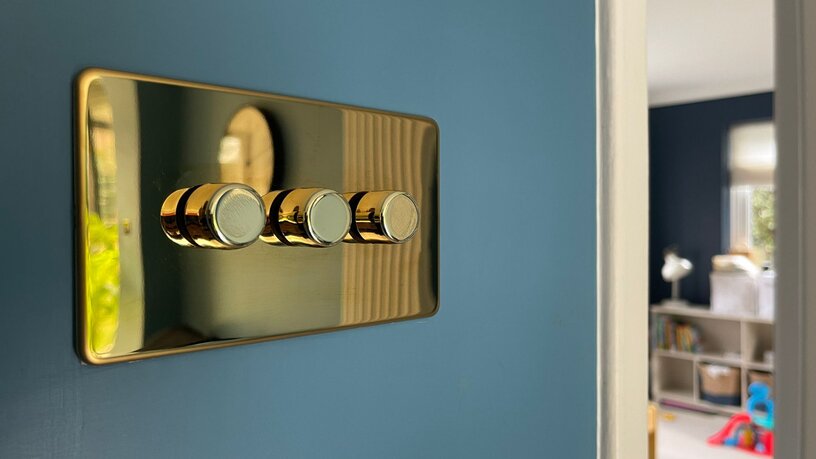
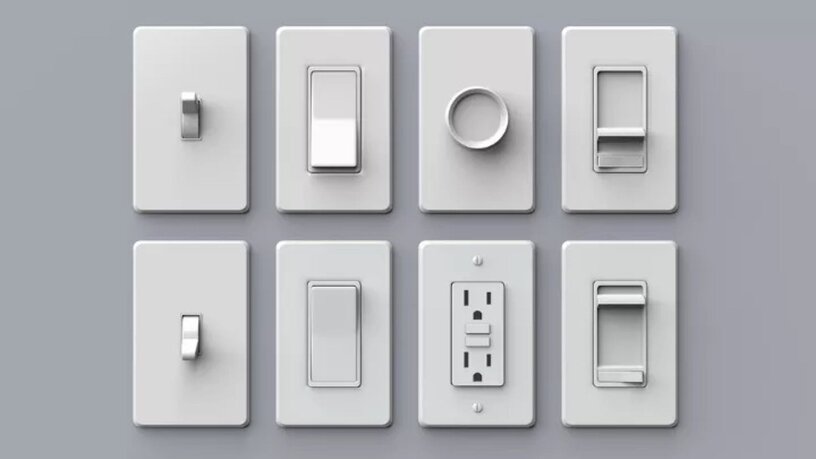
Wireless Dimming
- No need for physical wiring between the controller and module, making it easy to install.
- Supports wall plates, remote controls, and even smart home systems, allowing for synchronised and flexible control.
- Best suited for domestic or light commercial environments. However, it is not compatible with Building Management Systems (BMS).
Wired Dimming
- Reliable and long-established for commercial applications requiring centralised and precise lighting control.
- Compatible with BMS, offering seamless integration into advanced setups.
- Requires more extensive wiring and infrastructure but is highly dependable for large-scale systems.

Where to Dim
Understanding where to place dimming controls within a lighting system is key to achieving optimal performance and compatibility. Below are the primary placement options:
Before the Driver (TRIAC / Phase Cut Dimming)
- Typically used when integrating with existing wiring, especially where mains dimmers are already installed.
- Can be challenging to ensure compatibility between the driver and dimming wall plate, which may result in unexpected flickering.
After the Driver (Dimming Module)
- Placed between the driver and LEDs for better reliability compared to TRIAC dimming.
- Offers a wide range of compatible products and is ideal for retrofitting into existing LED systems.
- Requires additional infrastructure and space for mounting controls.
Within the Driver (e.g., Syndeo Systems)
- A compact, plug-and-play option that simplifies installation and saves time on-site.
- Does not require additional wiring, making it suitable for non-specialist teams.
- Limited in the range of controls and accessories; replacing the whole system may be necessary for upgrades.

Control Protocols for LED Dimming
0-10V: A simple analogue protocol that adjusts brightness by varying voltage levels between 0 and 10 volts. It is commonly used for smaller installations due to its straightforward operation and affordability.
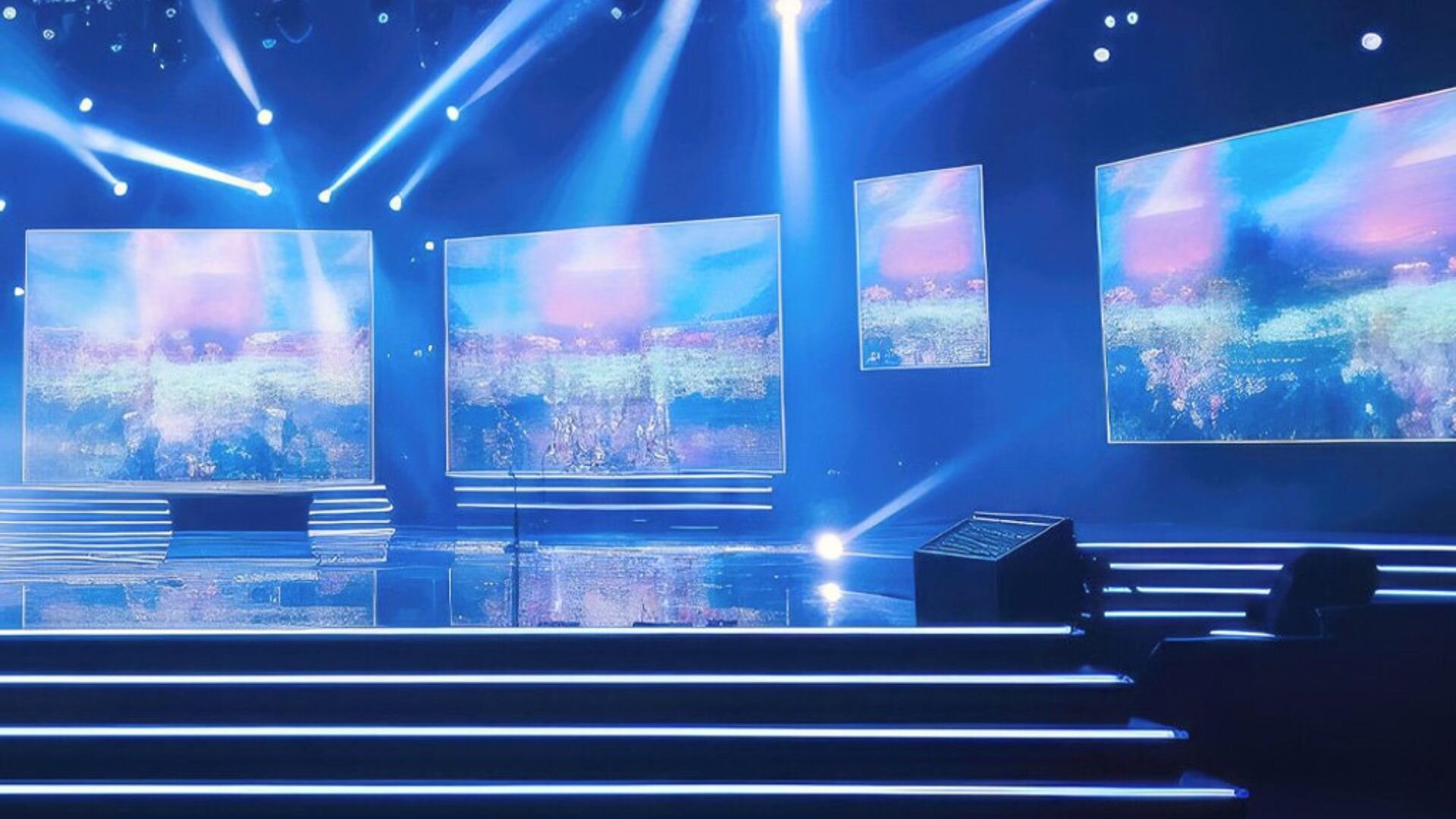
DMX: Widely used in entertainment and architectural lighting, DMX provides brightness, colour, and animation control. This protocol is essential for projects requiring advanced RGB controllers, offering seamless integration and dynamic effects.
DALI: A digital protocol designed for automated dimming and scheduling, DALI is ideal for commercial environments. It supports centralised control, making it suitable for large-scale projects requiring consistent and efficient lighting management.
Pixel Control: This protocol allows for individual LED control, enabling intricate animations and advanced effects. By utilising high-frequency PWM, pixel control ensures smooth and flicker-free operation, perfect for creative and artistic applications.

What Is Colour Control?
Colour control in LED lighting adjusts the intensity of individual colour channels—red, green, and blue—to create specific colours or tones. For instance, producing pink requires blending red with small amounts of blue and green.
This process involves dimming across multiple channels simultaneously, which allows for dynamic, customisable lighting designs.
Advanced control protocols like DMX or DALI enable seamless colour transitions and consistent results in applications such as architectural, theatrical, or ambient lighting projects.

Flickering & Camera Sensitivity
In certain environments, PWM dimming can cause flickering that’s invisible to the naked eye but noticeable when filmed.
This occurs when the PWM frequency aligns with a camera’s shutter speed, making it problematic for TV production, photography, and other camera-sensitive applications.
To prevent this, it’s essential to use high-frequency PWM drivers. For installations involving cameras, select dimming controllers with adjustable PWM frequencies to ensure compatibility with shutter speeds and eliminate strobing effects.

Applications of LED Dimming
LED dimming plays a vital role in enhancing functionality and aesthetics across various environments. Here's how it is used:
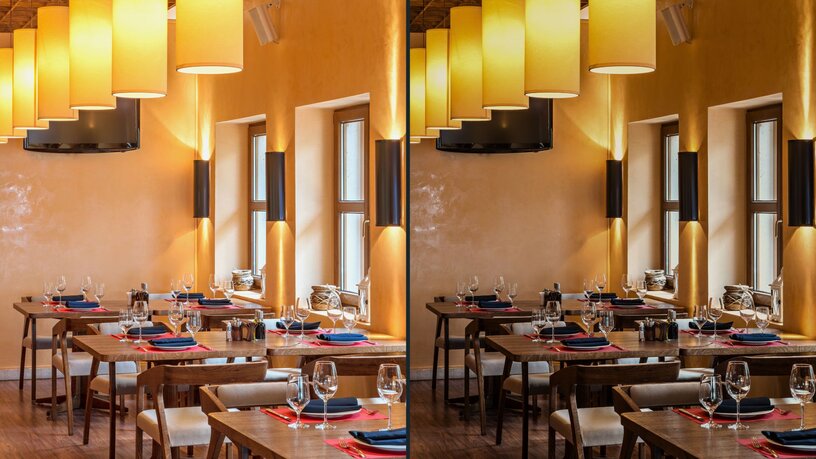
- Hospitality: Dim-to-warm LEDs help create inviting atmospheres in restaurants, hotels, and event spaces. The ability to adjust colour temperatures enhances the mood and complements the setting.
- Retail: Adjustable lighting improves product visibility and highlights key displays, enhancing the overall shopping experience. Dimming also allows flexibility to adapt lighting to different times of the day.
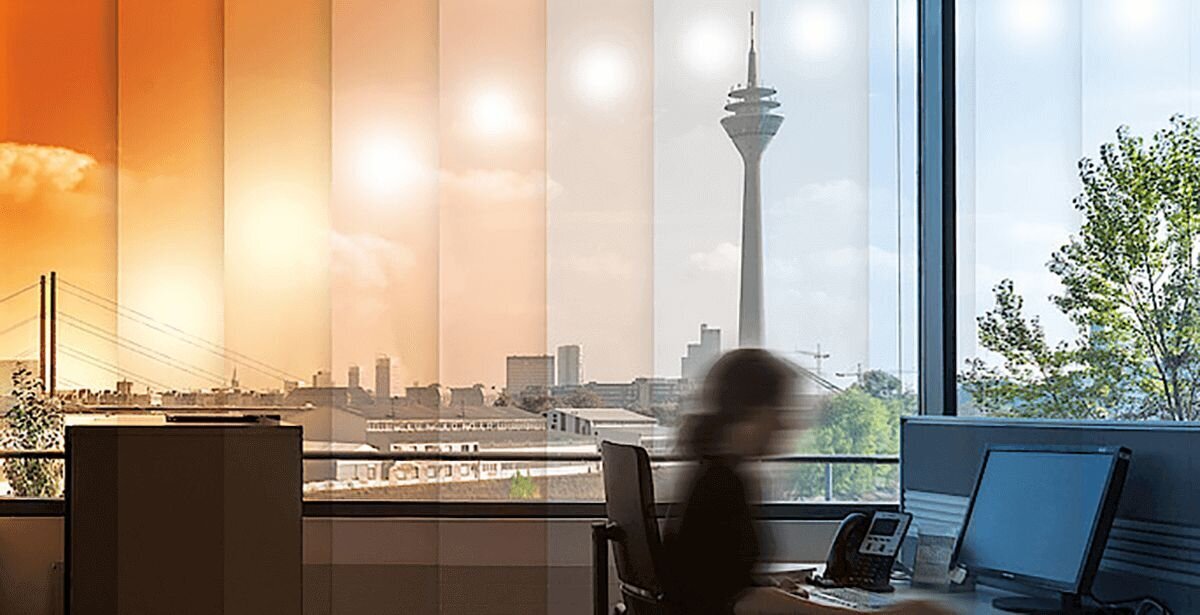
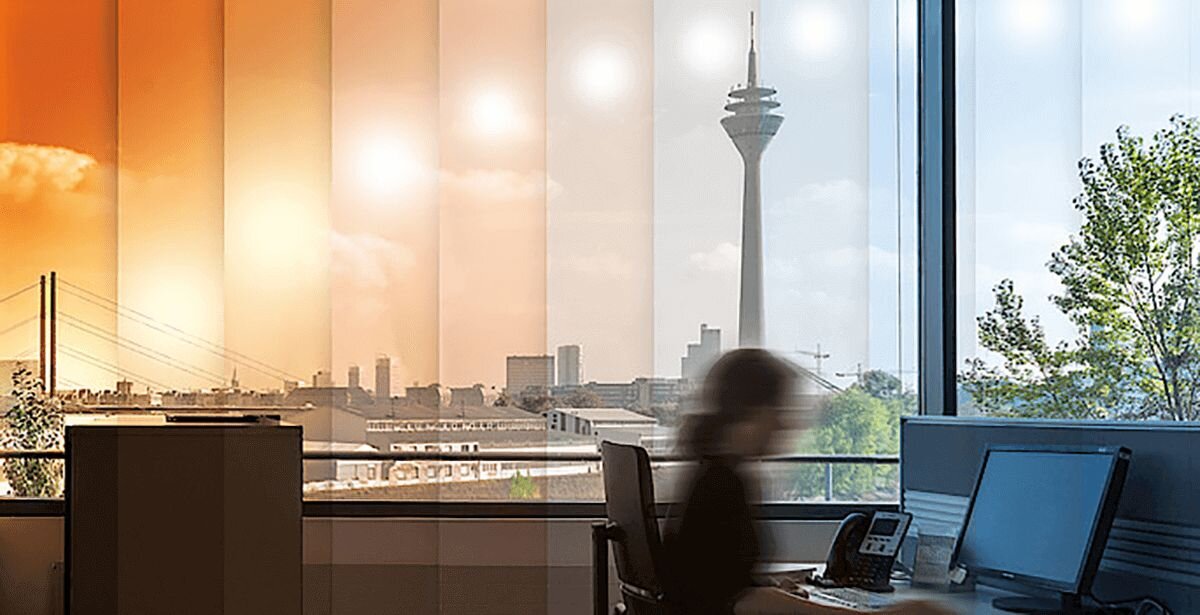
- Architecture: Tunable white LEDs are widely used in modern architecture to enable dynamic lighting designs. They provide flexibility to adjust brightness and colour temperatures, complementing the design and purpose of the space.
- Human-Centric Lighting: Dimming technology supports human-centric lighting, aligning with natural circadian rhythms. For example, brighter, cooler light during the day can boost focus, while warmer tones in the evening promote relaxation.

FAQs
Can I use a standard dimmer for LED lights?
Yes, you can use a TRIAC dimmer with a phase-cut driver, but it's essential to check the manufacturer's data sheet for compatibility to avoid potential issues.
Why do my LEDs flicker when dimmed?
Flickering often occurs due to low PWM frequencies or incompatible dimming drivers. High-frequency PWM drivers can resolve this issue, ensuring a smooth and consistent dimming experience.
How do you control dimming?
Dimming is controlled using protocols like 0-10V, DMX, DALI, and pixel control, with options including remote controls, touch panels, and rotary dimmers.
Why do my lights flash when I change the dimming level?
This often happens when a dimmer is wired after a driver with an integrated dimmer, causing instability. Long-run tapes with ICs can also cause pulsing, which can be resolved by adjusting the PWM frequency or changing the tape.
Why is my dimmer unstable?
Dimmer instability is often due to the dimmer being wired too close to the driver, causing interference. Ensure a minimum spacing of 250mm between the driver and dimmer.
Explore Ultra LEDs’ range of LED strips, drivers, and accessories to ensure your next project meets the highest standards of performance and reliability.
Get in touch with Ultra LEDs today
Ready to achieve exceptional colour accuracy in your next LED installation? Contact Ultra LEDs to find the ideal lighting solutions for your needs.
George Davies, the Director of Pecelec Studio Ltd, contributed to this blog with his expertise in electronics design and LED lighting. Pecelec Studio Ltd specialises in delivering high-performance LED solutions and advanced electronic systems for architectural, artistic, and experiential projects.